L-NAME hydrochloride
CAS No. 51298-62-5
L-NAME hydrochloride( NG-Nitroarginine methyl ester hydrochloride )
Catalog No. M14773 CAS No. 51298-62-5
A widely used inhibitor of NO synthase (NOS) with IC50 of 70 uM for purified brain NOS.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 68 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameL-NAME hydrochloride
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA widely used inhibitor of NO synthase (NOS) with IC50 of 70 uM for purified brain NOS.
-
DescriptionA widely used inhibitor of NO synthase (NOS) with IC50 of 70 uM for purified brain NOS; inhibits cGMP formation in endothelial cells with an IC50 of 3.1 μM (in the presence of 30 μM arginine) and reverses the vasodilation effects of acetylcholine in rat aorta rings.Asthma Phase 3 Clinical(In Vitro):L-arginine analogues are widely used inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity, with Nw-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) being at the head. Freshly dissolved L-NAME is a 50 fold less potent inhibitor of purified brain NOS (mean IC50= 70 μM) than L-NOARG (IC50= 1.4 μM), but the apparent inhibitory potency of L-NAME approached that of L-NOARG upon prolonged incubation at neutral or alkaline pH. HPLC analyses reveal that NOS inhibition by L-NAME closely correlated with hydrolysis of the drug to L-NOARG. (In Vivo):L-NAME infusion significantly decreases NKT-leukocyte level, tumor-necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha production by T-splenocytes and macrophages, and IFNγ production by T-leukocytes, monocytes, and T-splenocytes, as well as increased interleukin-6 production by T-leukocytes and monocytes and nitrate/nitrite production by T-leukocytes. There is increasing evidence that nitric oxide may be involved in learning and memory. l-NAME produces a task-dependent impairment of fear extinction, and implies that nitric oxide signaling is involved in memory process of certain fear extinction tasks. Chronic L-NAME administration induces cardiac hypertrophy in rodent models. Six weeks L-NAME administration induces significant cardiac hypertrophy compared to control hearts.
-
In VitroL-arginine analogues are widely used inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity, with Nw-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) being at the head. Freshly dissolved L-NAME is a 50 fold less potent inhibitor of purified brain NOS (mean IC50= 70 μM) than L-NOARG (IC50= 1.4 μM), but the apparent inhibitory potency of L-NAME approached that of L-NOARG upon prolonged incubation at neutral or alkaline pH. HPLC analyses reveal that NOS inhibition by L-NAME closely correlated with hydrolysis of the drug to L-NOARG.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsNG-Nitroarginine methyl ester hydrochloride
-
PathwayImmunology/Inflammation
-
TargetNOS
-
RecptoreNOS|iNOS|nNOS
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
IndicationAsthma
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number51298-62-5
-
Formula Weight269.686
-
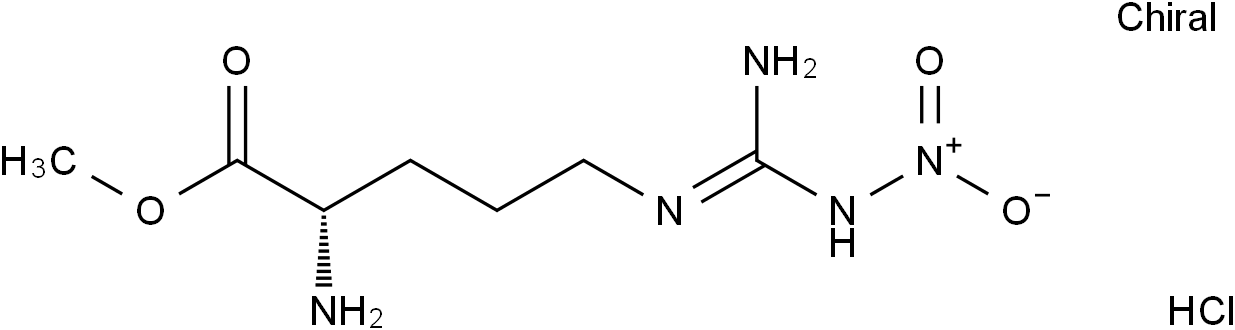
Molecular FormulaC7H16ClN5O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityH2O: ≥ 32 mg/mL
-
SMILESCOC(=O)[C@H](CCCN=C(N)N[N+](=O)[O-])N.Cl
-
Chemical NameL-Ornithine, N5-[imino(nitroamino)methyl]-, methyl ester, hydrochloride (1:1)
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Pfeiffer S, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Jul;118(6):1433-40.
2. Lo HC, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 23;11(3):e0151973.
3. Xiao H, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 May 2;8(18):29976-29983.
molnova catalog



related products
-
4-Hydroxyflavanone
4-Hydroxyflavanone is a natural product shows full vasorelaxing effects.
-
ZLc002
ZLc002 (ZLc-002) is a putative small-molecule inhibitor of nNOS interaction with NOS1AP.
-
S-Methylisothiourea ...
S-Methylisothiourea sulfate ((S)-Methylisothiourea sulfate) is a potent and selective inhibitor of iNOS and exerts beneficial effects in rodent models of septic shock.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


